Mechanical watches are not just timekeeping devices; they are intricate pieces of engineering that blend artistry with precision. This article dives deep into the inner workings of mechanical watches, exploring their components, mechanisms, and the fascinating principles that govern their operation.
Introduction to Mechanical Watches
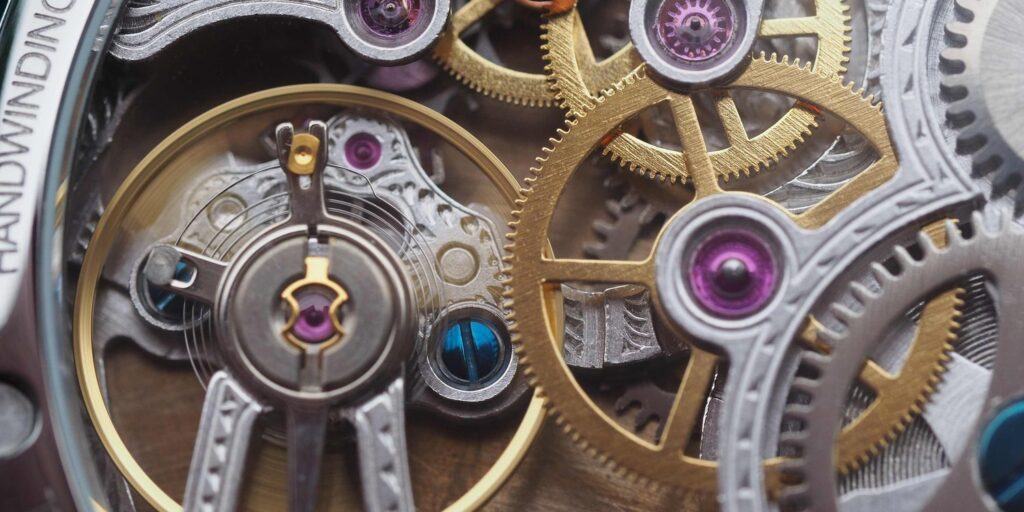
Mechanical watches have enchanted wearers for centuries with their craftsmanship and reliability. Unlike their electronic counterparts, mechanical watches derive their power from a mainspring, a tightly wound coil of metal that stores energy. This stored energy is released gradually to power the watch’s movement, which drives the hands around the dial.
The Main Components of a Mechanical Watch
- Mainspring: The heart of a mechanical watch, the mainspring stores potential energy when wound.
- Gear Train: A series of gears that transmit energy from the mainspring to the escapement.
- Escapement Mechanism: Regulates the release of energy from the mainspring to the balance wheel.
- Balance Wheel: Oscillates back and forth, acting as the timekeeping element.
- Hands and Dial: Display the time through the motion of the gears and escapement.
Understanding the Mechanism: Step-by-Step
- Winding the Watch: Turning the crown winds the mainspring, storing energy.
- Manual vs. Automatic: Manual watches require winding by hand, while automatic watches wind themselves through the motion of the wearer’s wrist.
- Energy Transmission: The mainspring’s energy is transmitted through the gear train, which consists of multiple gears of varying sizes. This transmission reduces the speed of rotation while increasing torque.
- Escapement Action: The escapement, typically a lever with a pallet fork interacting with the escape wheel, controls the release of energy in precise increments.
- Balance Wheel Oscillation: The escapement releases energy in impulses that cause the balance wheel to oscillate back and forth at a constant rate. This rate is typically several times per second, depending on the watch’s design and movement.
- Timekeeping Regulation: The rate at which the balance wheel oscillates determines the watch’s accuracy. Adjustments to the balance wheel’s length or weight can fine-tune this rate.
- Transferring Motion to the Hands: The oscillation of the balance wheel is translated through a series of gears to move the watch hands around the dial, indicating the passage of time.

Types of Mechanical Movements
- Manual Mechanical Movements: Fully reliant on manual winding, these movements often appeal to enthusiasts who appreciate the ritual of winding their watch.
- Automatic Mechanical Movements: Also known as self-winding movements, these watches use the natural motion of the wearer’s wrist to wind the mainspring through a rotor mechanism.
The Artistry of Watchmaking
- Craftsmanship: Skilled artisans assemble mechanical watches by hand, ensuring each component fits precisely and operates smoothly.
- Decorative Techniques: Techniques like guilloché, engraving, and perlage adorn the movement’s visible surfaces, showcasing the watchmaker’s artistry.
Challenges and Innovations in Mechanical Watchmaking
- Precision Engineering: Achieving consistent accuracy in mechanical watches requires meticulous attention to detail and advanced manufacturing techniques.
- Innovative Materials: Modern watchmakers experiment with materials like silicon for escapements and balance springs to improve performance and reduce friction.
Conclusion
Mechanical watches represent a harmonious blend of tradition, craftsmanship, and engineering. Understanding their inner workings not only deepens appreciation for their complexity but also underscores their enduring appeal in a world increasingly dominated by digital technology. Whether manual or automatic, each mechanical watch tells a story of precision, artistry, and timeless elegance.
In conclusion, the allure of mechanical watches lies not only in their ability to keep time but also in the intricate mechanisms that power them. From the mainspring to the escapement and balance wheel, every component plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate timekeeping and enduring craftsmanship. As technology evolves, mechanical watches continue to captivate enthusiasts with their blend of tradition, innovation, and timeless elegance.
3.5